Production of fast charger for phone/laptop with USB-C
July 10, 2025I like to go on car trips and camping. But I also need to work, and I need electricity to do that. I use an ordinary car battery as a power source and it is from this battery that I need to charge my power bank, phone or laptop. Charging a power bank can be relatively simple. Charging a phone, if you want it fast, is more complicated. If you need to charge a laptop, you already have to think about it, and in this very article, I'll describe how to make an efficient car battery charger.
First of all, let's be clear about the terms. I use the word charger in the introduction, but what you have with your phone is not a charger. It's a USB power supply. What actually charges the battery in the phone is the electronics located right in the phone. That little box with the USB connector is the device that is capable of delivering the necessary current and voltage.
A little history
It used to be that every phone had a different connector and if you figured out the parameters of the power supply, you could make your own power supply. However, you would have to have a box full of such power supplies, plus a handful of connectors and reducers.
USB became a relatively standard connector. Gradually, therefore, phones used the USB connector as a charging connector. Even my first smartphone Open Moko Neo FreeRunner was charged from a USB mini connector. It was just one of the first phones to charge exclusively via USB, before the European Union made it standard. In fact, in the beginning, the first phones had USB, but they still had a power connector. Subsequently, USB became more or less the standard for charging. And the European Union introduced micro USB as the standard power connector. Today, the USB-C connector is used, which has the advantage, among other things, that you can plug it in any orientation.
However, today's phones have much higher power consumption and also their batteries have a larger capacity. That means you need to charge them more often and you want to recharge them quickly so you can use your phone immediately. The consequence is that you need to deliver much more power to your phone, and in much less time. Getting enough power to your phone is no longer trivial, and a simple USB power supply is no longer enough.
If you need to power something from USB, any 5V stabilizer will do. However, a regular stabilizer has a lot of power consumption and gets hot. Better to use a step-up or step-down pulse stabilizer, which has much more efficiency. A pulse stabilizer is also in this car-socket power supply. As a skilled electrical engineer, I modified the device in question to output 5V and connected the USB connector to the cable.
The pulse regulator is also in this special power supply with reduction, which I designed and implemented myself. I subsequently made a few more pieces for friends.
When I had Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Carbon laptops or the TUXEDO Pulse 15, I made a cable that I could clamp to a 12V car battery with a connector for the laptop. My voltage from 12V to 19V was provided by a pulse step-up regulator. The whole solution is small and very efficient. It makes no sense to use an inverter from 12V to 230V and then plug in a laptop power supply, as that is an inefficient solution.
Here is a pulse adjustable step-up stabilizer with a laptop connector. Cooler side:
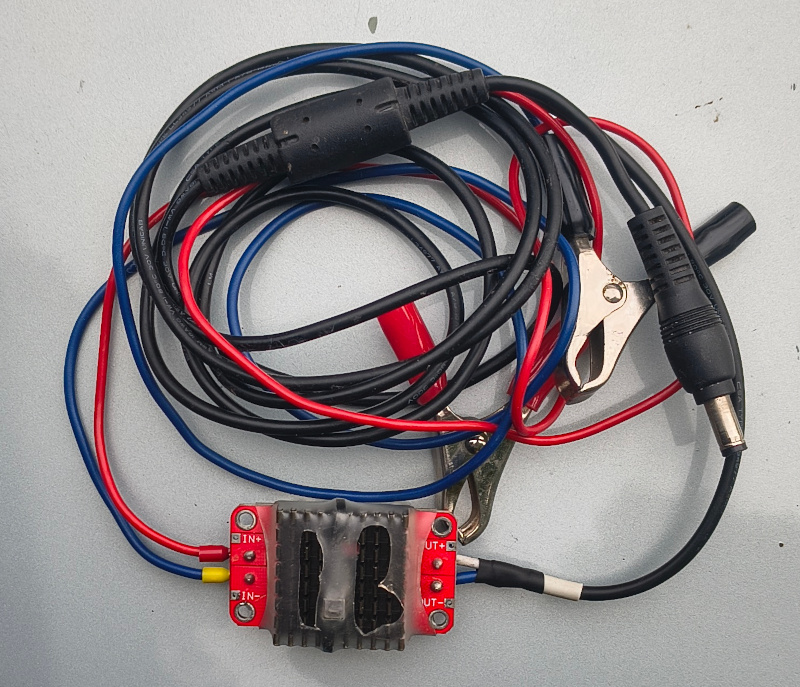
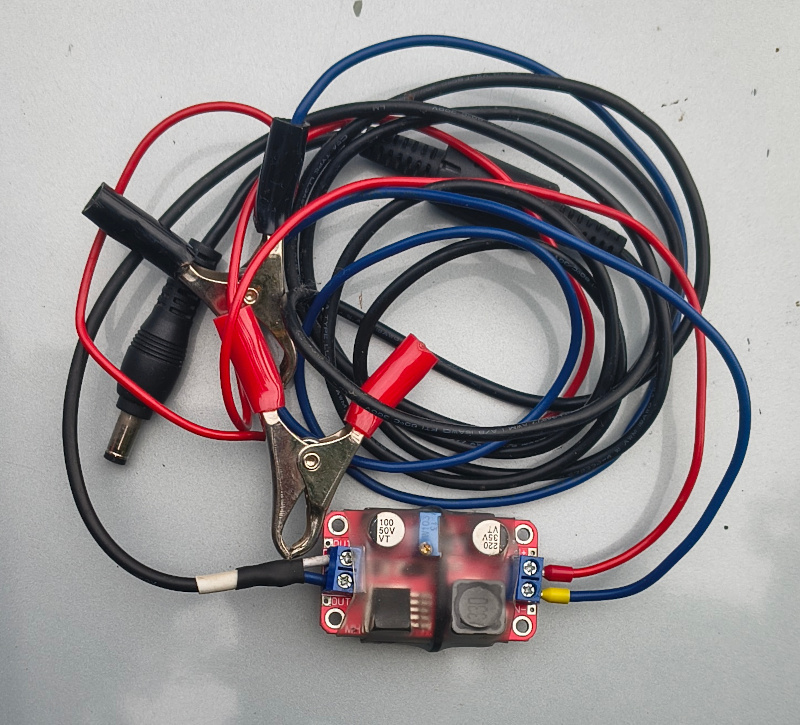
Pulse adjustable step-up stabilizer. Side with electronics and potentiometer to adjust output voltage:
New laptop
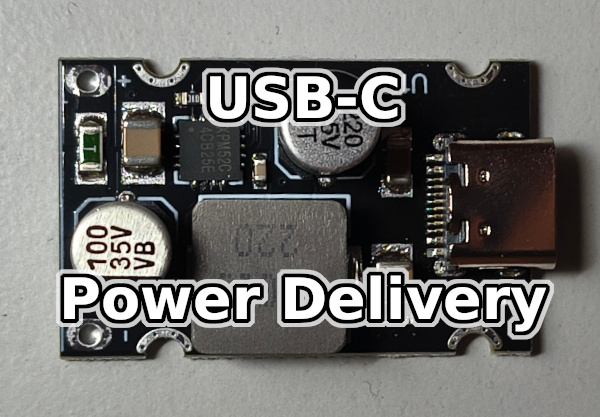
I now have a new laptop for work that only has USB-C for power and requires Power Delivery. Therefore, I can no longer use a regular power supply. So I started to solve how to power this new work computer alternatively e.g. from a battery.
What is Power Delivery (PD)
Power Delivery (PD) is the standard for fast charging via USB-C. It enables higher power (voltage and current) than conventional USB charging and intelligent communication between the charger and device.
Main Features of Power Delivery:
- 📶 Bidirectional communication: USB power supply and device "talk" - agreeing on ideal performance.
- ⚡ Higher Power: Supports up to 240 W (originally 100 W) - also suitable for laptops.
- 🔄 Bidirectional Power: Power can flow from laptop to phone and vice versa.
- 🔌 Universality: One USB-C cable can power phones, tablets, laptops, monitors and other devices.
Note: USB PD is mainly used with the USB-C connector, but can work over other connectors when specific implementation.
What Power Delivery is used for:
- Charging phones and laptops (e.g. MacBook, Dell XPS, Lenovo Thinkpad).
- Power monitors and docking stations via USB-C.
- Reduce the number of chargers and cables - one adapter for everything.
In practice, this means that I power my laptop from the monitor when working at home and I don't use the original power supply for the laptop. I use the powerful USB power supply from my phone to power my laptop when I travel, because this power supply is small and light and has sufficient power.
What the USB power supply supports can be found in the documentation and is often also indicated on the label of the USB power supply. Look for "USB-C PD", "Power Delivery", and look for the maximum power rating of the USB power supply (charger), for example 65W PD. The voltage it can provide is also crucial information, as laptops need 19 V - suitable USB power supplies are usually listed as 20 V.
Examples of performance:
| Voltage | Current | Power |
|---|---|---|
| 5 V | 3 A | 15 W |
| 9 V | 3 A | 27 W |
| 20 V | 5 A | 100 W |
| 48 V | 5 A | 240 W (USB PD 3.1 Extended) |
A cell phone power supply that can't power a laptop, but can recharge a phone quickly:

A mobile phone power supply that can also power a laptop. Because it can provide even 20 V at the output.

Original power supply for Lenovo Thinkpad notebook:

Versatile USB Power Delivery (USB PD)
| Beliefs | Year of issue | Maximum performance | Main Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| USB PD 1.0 | 2012 | 10 W - 100 W (5 V to 20 V, 2 A to 5 A) | Basic voltage switching; limited compatibility |
| USB PD 2.0 | 2014 | 100 W | Integration with USB Type-C; introduction of voltage and current profiles |
| USB PD 3.0 | 2015 | 100 W | Introduction of PPS (Programmable Power Supply), better charge management |
| USB PD 3.1 | 2021 | 240 W (Extended Power Range - EPR) | Extended Power (48V, 5A), support for larger devices such as laptops |
What is Quick Charge
There is still Quick Charge technology. Quick Charge is a fast charging technology from Qualcomm, designed primarily for for devices with their processors (e.g. Snapdragon). It allows you to reduce the charging time of your phone or tablet by by increasing the voltage or current.
Main Features:
- ⚡ Faster charging than standard USB
- 🔌 Works via standard USB-A or USB-C (depending on version)
- 📱 Most common in phones with Qualcomm Snapdragon chips
- 🔋 Compatible devices will talk to the charger and select the ideal voltage
Quick Charge version overview:
| Beliefs | Maximum performance | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| QC 1.0 | 10 W | Higher current only |
| QC 2.0 | 18 W | Introduction of higher voltage (5V, 9V, 12V) |
| QC 3.0 | 18 W | Dynamic voltage (3.6V-20V) |
| QC 4.0 / 4+ | 27 W and above | USB Power Delivery support |
| QC 5.0 | 100 W+ | Very fast charging, USB PD support, multiple cells simultaneously |
Quick Charge vs Power Delivery Comparison
- Quick Charge is Qualcomm's closed standard
- Power Delivery is open and more versatile
- Both technologies can work together - QC 4.0+ also supports USB PD
Notebook Power Connector
A typical laptop power connector has a round shape and a voltage of 19 V.
It is usually called a DC connector 🔌.
However, it may not always be the same, nor round.
Many HP, Asus and Acer laptops had the same connector with the same polarity and voltage of 19 V.
Thus, I was able to use the power supplies from these laptops in my compal FL90 laptop.
However, the same-looking connectors may not be compatible - they may differ in size and polarity.
Some connectors contain a smart chip or a third contact (e.g. Dell).
🧾 Basic information:
- Used in notebook power adapters, often with a voltage of 19 V.
- Typical designation: DC connector or barrel connector.
- Consists of outer cylindrical shell and inside pin.
- Dimensions are given as inner diameter × outer diameter - e.g.
5.5 × 2.5 mm.
📦 Examples of dimensions (by manufacturer):
| Manufacturer | Connect dimensions (mm) | Note |
|---|---|---|
| HP | 4.8 × 1.7 or 7.4 × 5.0 | Newer ones have a blue centre |
| Lenovo | 5.5×2.5/USB-C | Older models have barrel, newer USB-C |
| Dell | 7.4×5.0 | With center pin |
| ASUS/Acer | 5.5 × 2.5 or 4.0 × 1.35 | Depends on model |
| Toshiba | 5.5 × 2.5 | Standard size |
Lenovo ThinkPad power connectors
The company with the most confusion in connectors is IBM, later Lenovo, which almost always used some special type of connector. Lenovo ThinkPad laptops have used different types of power connectors in different generations. See below for a basic overview.
1. 🔌 Round DC connector (barrel connector)
In old laptops, it had a big yellow round connector.
- Period: until about 2013 (e.g. ThinkPad T410, T420, T530)
- Dimension: 7.9 mm outer / 5.5 mm inner diameter with center pin
- Voltage: 20 V
- Note: Appearance similar to other brands but may not be compatible
2. 🟨 Rectangular "Slim Tip" (yellow connector)
She subsequently switched to a very atypical square connector.
- Period: from approx. 2013 (e.g. T440, T460, T480, X260, L580)
- Shape: rectangular, yellow plastic inside
- Voltage: 20 V
- Name: Lenovo Slim Tip / Rectangular Tip
- Wattage: 45W, 65W, 90W, 135W adapters
3. ⚡ USB-C (Power Delivery)
Fortunately, today it has switched to standard USB-C
- Period: from approx. 2018-2019 (e.g. T490, T14, X1 Carbon Gen 6+)
- Standard: USB-C Power Delivery (PD)
- Advantage: Universal for multiple devices (laptop, phone, tablet)
- Power: typically 65W or 100W PD adapter
Important for proper laptop power
To properly power your laptop, it is important to ensure that the power adapter matches the requirements of the device. The key parameters are voltage (V), current (A) and connector type. The voltage must be the same as the notebook requirements, the current may be lower than that specified on the delivery original power supply, but then the laptop will not need to be recharged if the laptop is operated at maximum power. It is also necessary to observe correct connector polarity - most laptops have plus inside and minus outside. Using the wrong adapter can lead to non-functionality, damage to the battery or the device itself. It is recommended to use original or certified replacement power supplies. But the expert can can handle non-certified power supplies.
Power your laptop from a lead-acid car battery on the road
When travelling, powering a laptop is often a challenge, especially when a conventional power outlet is not available. An older lead acid car battery is an effective solution for powering a laptop. However, because the voltage of a lead-acid battery is usually lower (12 V), it is necessary to use a DC-DC converter, which converts the voltage to the values needed for the laptop, usually 19 V or 20 V, depending on the model of the device.
Next, it is important to select the correct cable and connector that matches the laptop's power input, and make sure, that the inverter provides sufficient power (for example, 60 W, 90 W or more depending on the laptop's requirements). Inverters should have also overload, overvoltage and short circuit protection for safe use.
With a quality DC-DC converter and matching battery, the laptop can be powered even on long trips away from civilization, but it's always good to remember that lead acid batteries are heavy and have a limited capacity, so it's important to plan charging and endurance so that the continued operation of the device is not compromised.
Power your laptop from a battery on the go
If your laptop is powered by USB-C., a power bank with sufficient capacity and power. To ensure compatibility, it is important that the power bank supports output voltage matching the requirements laptop - typically 20V via USB-C Power Delivery or voltage switchable DC output. A suitable cable must also be provided. Any USB-C cable cannot be used.
I bought a special plate with electronics that works as a step-up step-down pulser for these cells stabilizer and supports Power Delivery, thanks to the XPM52C chip. So with a min 20V input voltage, it should provide up to 65W of power for running or charging.
Plate purchased on Aliexpress:
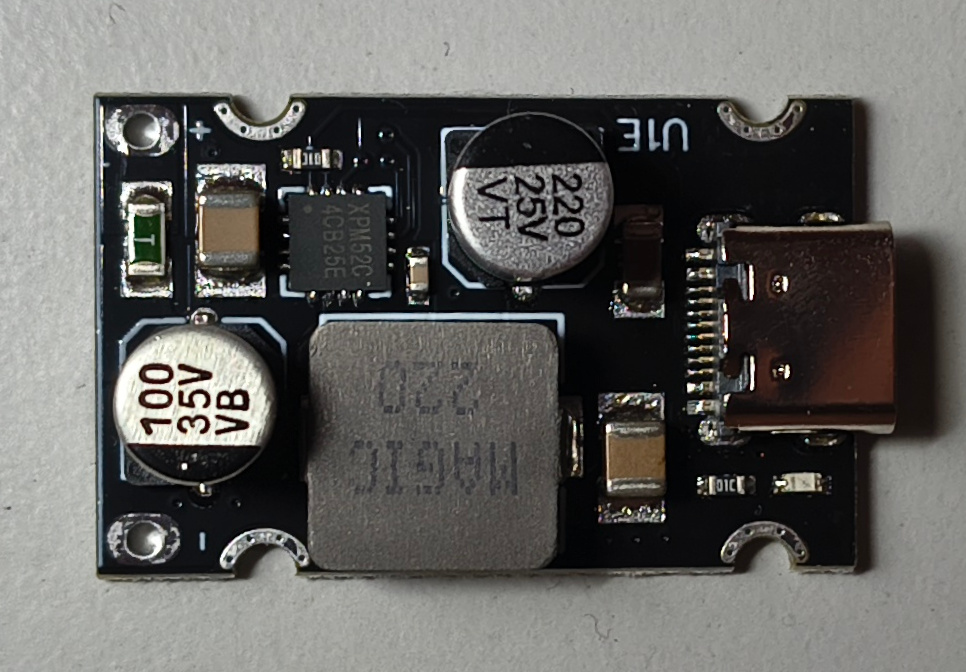
When plugged into a 12V battery, it can power my new Lenovo Thinkpad P14S work laptop with no problem.
Customized solution
You too can make a power supply to suit your needs. You will need to study some electrical and electrical engineering and read the documentation.
Yes, I studied at CTU, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, and I have been involved in electrical engineering for years. However, I do not offer development of electrical engineering projects. I now provide services primarily in the IT area. So if you want to tackle an electrical engineering project, I can participate from an architecture and software development perspective. For electronics development, I only provide consultation. You can contact me via email or contact form.
Articles on a similar topic
Newsletter
If you are interested in receiving occasional news by email.
You can register by filling in your email
news subscription.
+